Customize advanced system settings
Several features for advanced users are located on Administration > System Settings > Advanced.
You can automate system setting changes using the Deep Security API. For examples, see the Configure Policy, Computer, and System Settings guide in the Deep Security Automation Center.
Primary Tenant Access
By default, the primary tenant can access your Deep Security environment.
If the primary tenant enabled the "Primary Tenant Access" settings in your environment, however, you can prevent the primary tenant from accessing your Deep Security environment, or grant access for a limited amount of time.
Load Balancers
Agents are configured with a list of Deep Security Manager and Deep Security Relays. When multiple managers and relays are deployed
To better scale your network, you can put a load balancer in front of the managers or relays. When you configure the load balancer hostname and port numbers, it will override the IP address or hostname and port numbers currently used by the agents.
The script generator uses the address of the Deep Security Manager that you are connected to. This ensures that the scripts continue to function even if one of the Deep Security Manager nodes fails or is down for maintenance or upgrades.
Multi-tenant Mode
- Select Enable Multi-Tenant Mode.
- In the wizard that appears, enter your Multi-Tenant Activation Code and click Next.
- Select the license mode, either:
- Inherit Licensing from Primary Tenant: All tenants use the same licenses as the primary tenant.
- Per Tenant Licensing: Tenants themselves enter a license when they log in for the first time.
- Click Next.
Deep Security Manager Plug-ins
Plug-ins are modules, reports and other add-ons for the Deep Security Manager. Trend Micro occasionally produces new or additional versions of these which are distributed as self-installing packages.
SOAP Web Service API
Enable or disable the legacy SOAP API Web services. The WSDL (Web Services Description Language) can be found at the URL displayed in the panel on the page. For more information about APIs, see Use the Deep Security API to automate tasks.
Status Monitoring API
Enable or disable the Status Monitoring API of the legacy REST API. This API lets you query the Deep Security Manager (including individual Manager Nodes) for status information such as CPU and memory usage, number of queued jobs, total and Tenant-specific database size. For more information about APIs, see Use the Deep Security API to automate tasks.
Export
Export file character encoding: The character encoding used when you export data files from the Deep Security Manager. The encoding must support characters in your chosen language.
Exported Diagnostics Package Language: Your support provider may ask you generate and send them a Deep Security diagnostics package. This setting specifies the language the package will be in. The diagnostic package is generated on Administration > System Information.
Whois
Whois can be used to look up which domain name is associated with an IP address when you review logged intrusion prevention and firewall events. Enter the search URL using "[IP]" as a placeholder for the IP address to look up.
(For example, "http://reports.internic.net/cgi/whois?whois_nic=[IP]&type=nameserver".)
Licenses
Hide unlicensed Protection Modules for new Users determines whether unlicensed modules are hidden rather than simply grayed out for subsequently created Users. (This setting can be overridden on a per-user basis on Administration > User Management > Users > Properties).
Click View Scan Cache Configurations to display a list of saved Scan Cache Configurations. Scan Cache Configurations are settings used by the Virtual Appliance to maximize the efficiency of Anti-Malware and Integrity Scans in a virtualized environment. See Virtual Appliance Scan Caching for more information.
CPU Usage During Recommendation Scans
This setting controls the amount of CPU resources dedicated to performing Recommendation Scans. If you notice that CPU usage is reaching unreasonably high levels, try changing to a lower setting to remedy the situation. For other performance controls, see Administration > Manager Nodes > Properties > Performance Profiles.
NSX
If Deep Security is being used to protect virtual machines in a VMware NSX environment and if it is installed with multiple Deep Security Manager nodes, this setting will determine which Deep Security Manager node communicates with the NSX Manager. (For more information on integrating Deep Security with an NSX environment, see Install Deep Security Manager. For more information on multiple Deep Security Manager Nodes, see Install Deep Security Manager on multiple nodes.
Logo
You can replace the Deep Security logo that appears on the login page, at the top right of the Deep Security Manager GUI, and at the top of reports. Your replacement image must be in PNG format, be 320 px wide and 35 px high, and have a file size smaller than 1 MB. A template is available in the installfiles directory of the Deep Security Manager.

Click Import Logo to import your own logo, or click Reset Logo to reset the logo to its default image.
Manager AWS Identity
You can configure cross-account access. Select either:
- Use Manager Instance Role: The more secure option to configure cross-account access. Attach a policy with the sts:AssumeRole permission to the Deep Security Manager's instance role, then select this option. Does not appear if the Deep Security Manager does not have an instance role, or if you're using an Azure Marketplace or on-premise installation of Deep Security Manager.
- Use AWS Access Keys: Create the keys and attach a policy with the sts:AssumeRole permission before you select this option, and then type the Access Key and Secret Key. Does not appear if you're using an Azure Marketplace or on-premise installation of Deep Security Manager.
Application control
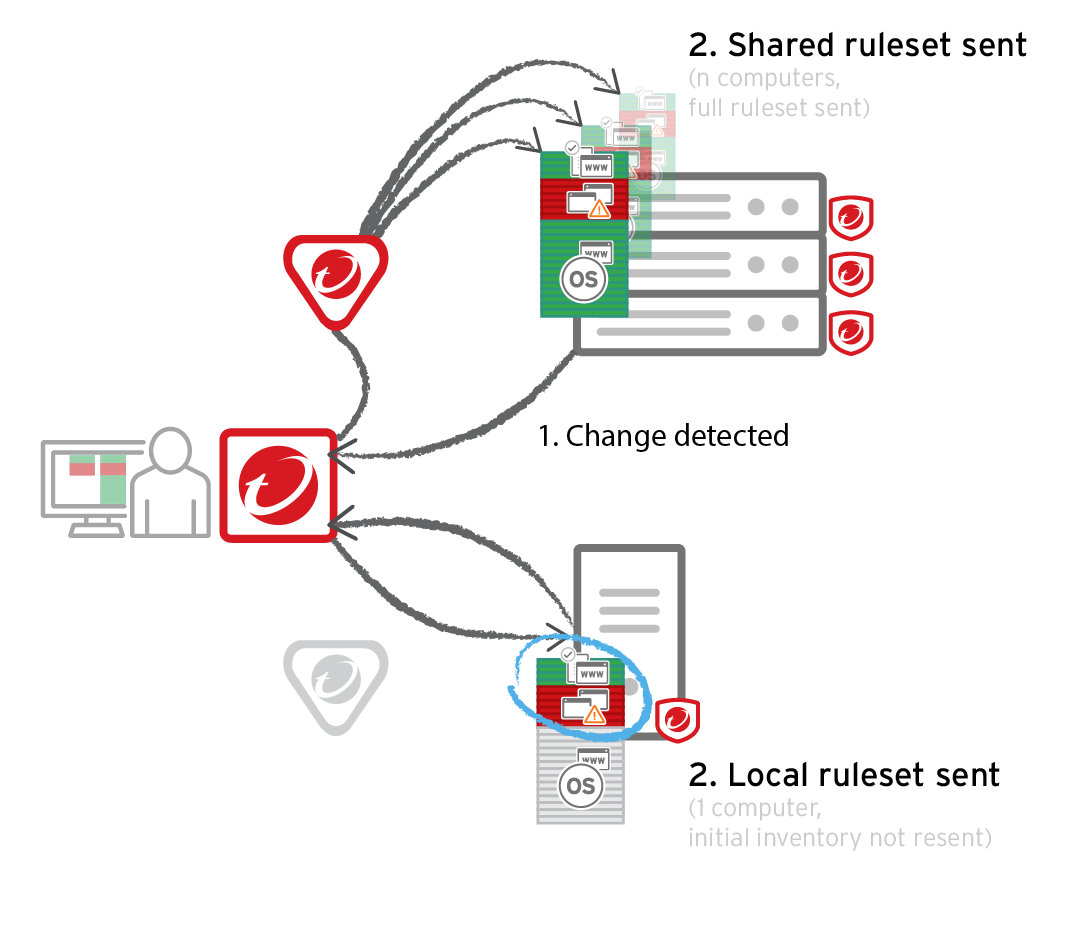
Each time you create an Application Control ruleset or change it, it must be distributed to all computers that use it. Shared rulesets are bigger than local rulesets. Shared rulesets are also often applied to many servers. If they all downloaded the ruleset directly from the manager at the same time, high load could cause slower performance. Global rulesets have the same considerations.
Using Deep Security Relays can solve this problem. (For information on configuring relays, see Deploy additional relays.)
Steps vary by whether or not you have a multi-tenant deployment.
Single tenant deployments
Go to Administration > System Settings > Advanced and then select Serve Application Control rulesets from relays.
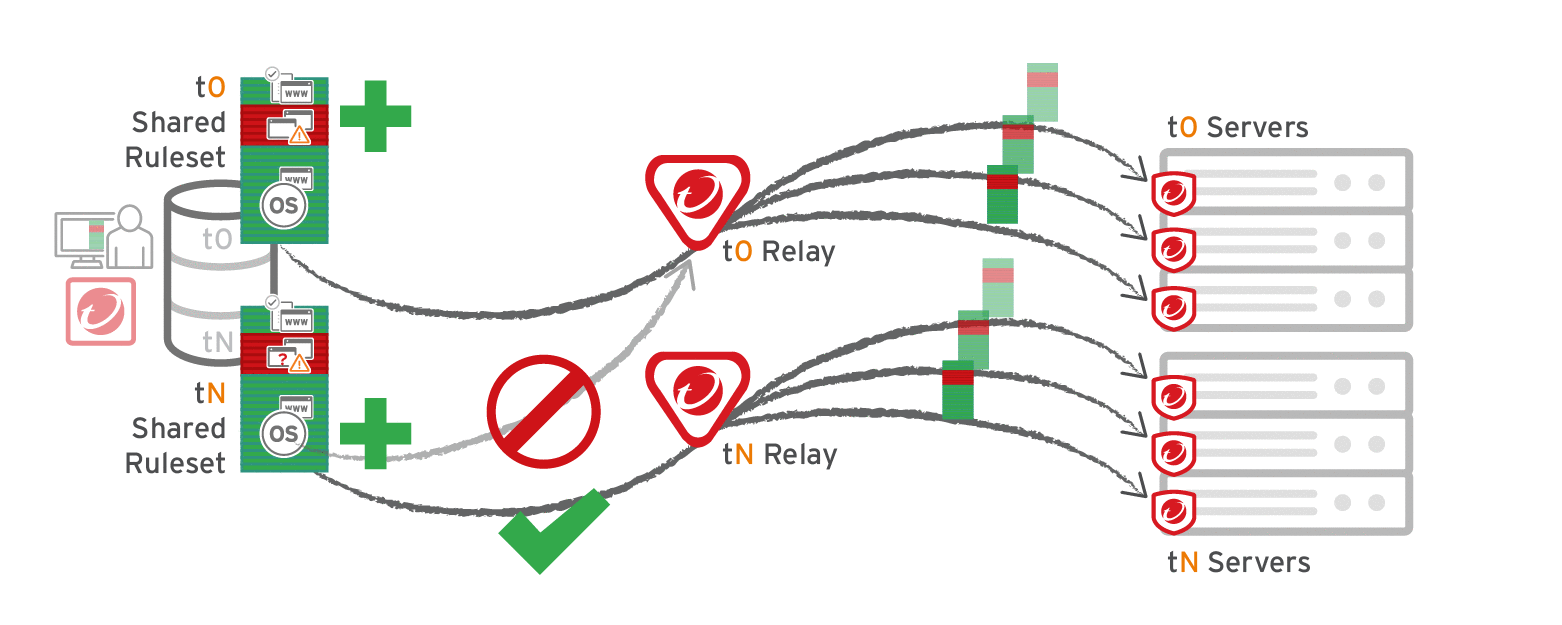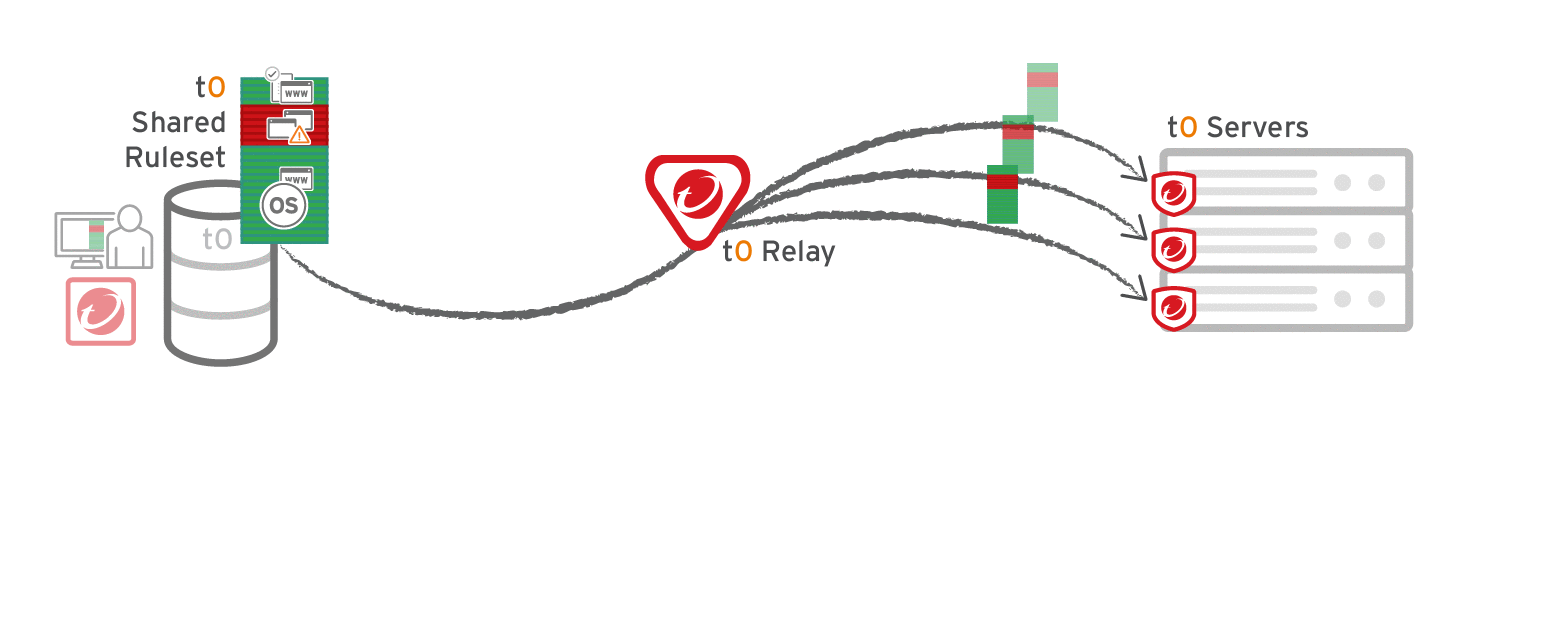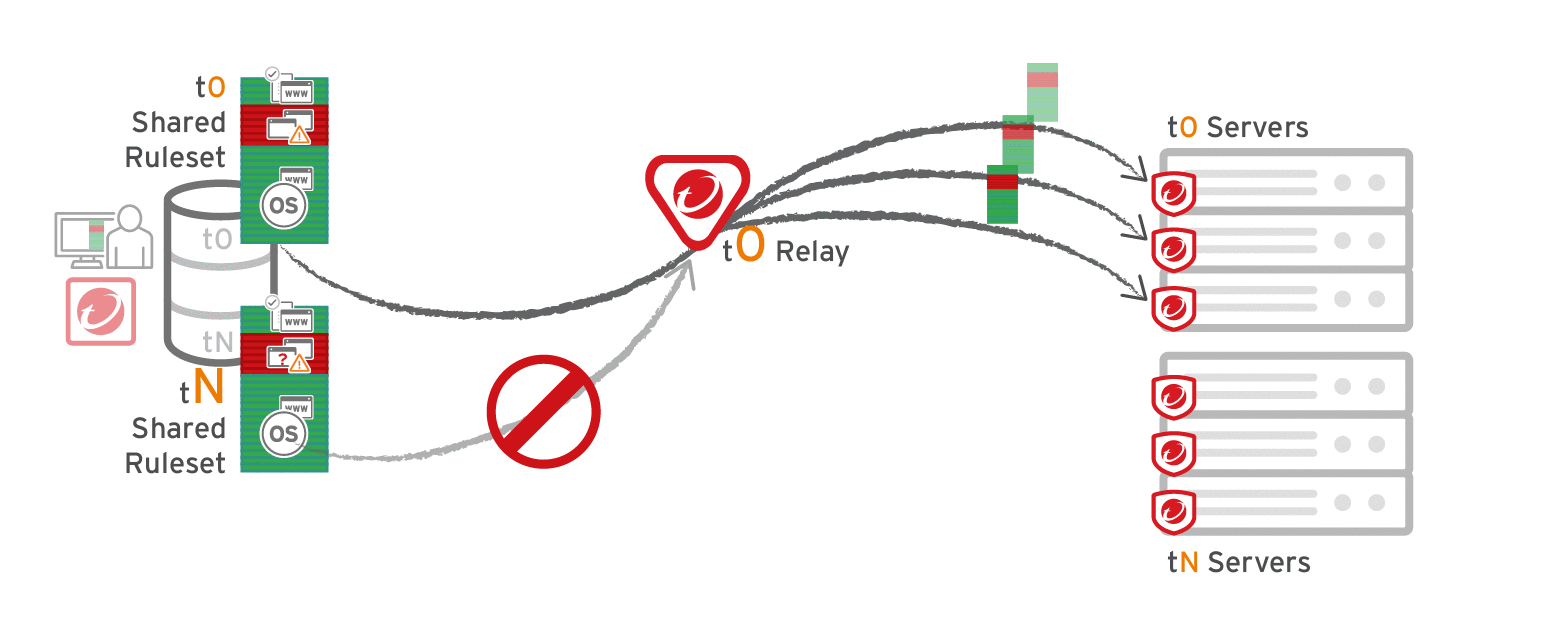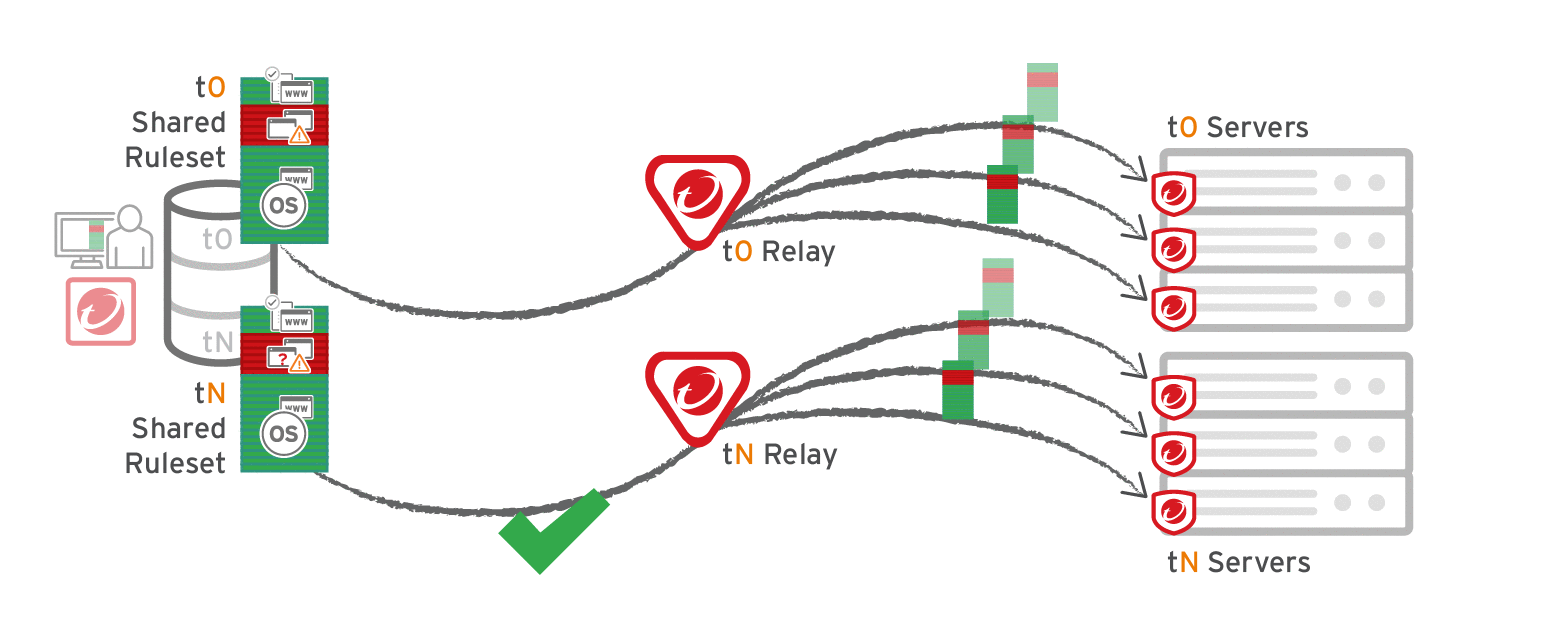
Multi-tenant deployments
The primary tenant (t0) can't access other tenants' (tN) configurations, so t0 relays don't have tN Application Control rulesets. (Other features like IPS don't have this consideration, because their rules come from Trend Micro, not a tenant.)
Other tenants (Tn) must create their own relay group, then select Serve Application Control rulesets from relays.
Verify compatibility with your deployment before using relays. If the agent doesn't have any previously downloaded rulesets currently in effect, and if it doesn't receive new Application Control rules, then the computer won't be protected by Application Control. If an Application Control ruleset fails to download, a ruleset download failure event will be recorded on the manager and on the agent.
Relays might either change performance, break Application Control ruleset downloads, or be required; it varies by proxy location, multi-tenancy, and global/shared vs. local rulesets.
| Required for... | Faster performance for... | Slower performance for... | Don't enable for... |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Agent > Proxy > Manager In Deep Security Agent 10.0 GM and earlier, agents didn't have support for connections through a proxy to relays. If a ruleset download fails due to a proxy, and if your agents require a proxy to access the relay or manager (including Deep Security as a Service), then you must either:
|
Shared rulesets Global ruleset |
Local rulesets |
Multi-tenant configurations when non-primary tenants (tN) use the default, primary (t0) relay group:
|