Set up Intrusion Prevention
Enable the Intrusion Prevention module and monitor network traffic for exploits using Detect mode. When you are satisfied with how your Intrusion Prevention rules are assigned, switch to Prevent mode.
- Enable Intrusion Prevention in Detect mode
- Test Intrusion Prevention
- Apply recommended rules
- Monitor your system
- Enable 'fail open' for packet or system failures
- Switch to Prevent mode
- Implement best practices for specific rules
- Apply NSX security tags
For an overview of the Intrusion Prevention module, see About Intrusion Prevention.
Enable Intrusion Prevention in Detect mode
Enable Intrusion Prevention and use Detect mode for monitoring. Configure Intrusion Prevention using the appropriate policies to affect the targeted computers. You can also configure individual computers:
- Go to Computer or Policy editor
 You can change these settings for a policy or for a specific computer.
To change the settings for a policy, go to the Polices page and double-click the policy that you want to edit (or select the policy and click Details).
To change the settings for a computer, go to the Computers page and double-click the computer that you want to edit (or select the computer and click Details). > Intrusion Prevention > General.
You can change these settings for a policy or for a specific computer.
To change the settings for a policy, go to the Polices page and double-click the policy that you want to edit (or select the policy and click Details).
To change the settings for a computer, go to the Computers page and double-click the computer that you want to edit (or select the computer and click Details). > Intrusion Prevention > General. - For Configuration, select either On or Inherited (On).
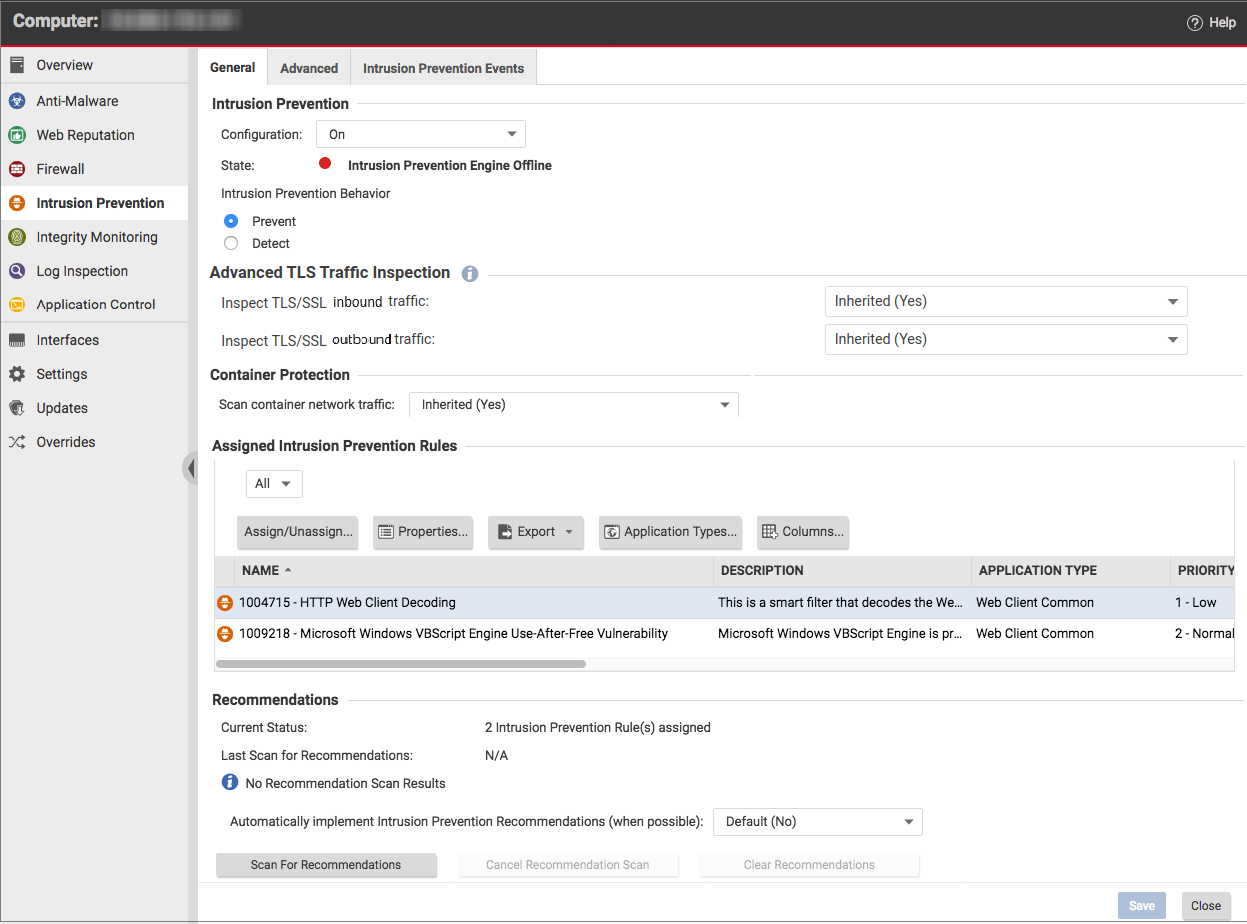
- For Intrusion Prevention Behavior, select Detect.
- With Deep Security Agent 11.1 and earlier, the Intrusion Prevention module inspects traffic that passes through the host computer's network interface to containers. With Deep Security Agent 11.2 or later, it can also inspect traffic between containers. When the Scan container network traffic setting is set to Yes, Deep Security scans the traffic that goes through both containers and hosts. When it is set to No, Deep Security scans only the traffic that goes through the host network interface.
- Click Save.
For more fine-grained control, when you assign Intrusion Prevention rules, you can override the global behavior mode and configure specific rules to either prevent or detect (see Override the behavior mode for a rule).
Test Intrusion Prevention
Before continuing, you should perform the following steps to verify that the Intrusion Prevention module is working properly:
- If you have an agent-based deployment, make sure you have a computer that has an agent running. For an agentless deployment, make sure your Deep Security Virtual Appliance is running normally.
- Disable the Web Reputation module. In Deep Security Manager, click Computers, then double-click the computer where you will test Intrusion Prevention. In the computer's dialog, click Web Reputation, and select Off. Web Reputation is now disabled and won't interfere with the Intrusion Prevention functionality.
- Make sure bad traffic is blocked. Still in the computer's dialog, click Intrusion Prevention, and under the General tab, select Prevent. (If it is shaded, set the Configuration drop-down list to Inherited (On).)
- Assign the EICAR test policy. Still in the computer's dialog, click Intrusion Prevention. Click Assign/Unassign. Search for 1005924. The 1005924 - Restrict Download of EICAR Test File Over HTTP policy appears. Select it and click OK. The policy is now assigned to the computer.
- Try to download the EICAR file (you cannot, if Intrusion Prevention is running properly). On Windows, go to this link: http://files.trendmicro.com/products/eicar-file/eicar.com. On Linux, enter this command: curl -O http://files.trendmicro.com/products/eicar-file/eicar.com
- Check the Intrusion Prevention events for the computer. Still in the computer's dialog box, click Intrusion Prevention > Intrusion Prevention Events. Click Get Events to see events that have occurred since the last heartbeat. An event appears with a Reason of 1005924 - Restrict Download of EICAR Test File Over HTTP. The presence of this event indicates that Intrusion Prevention is working.
- Revert your changes to return your system to its previous state. Turn on the Web Reputation module (if you turned it off), reset the Prevent or Detect option, and remove the EICAR policy from the computer.
Apply recommended rules
To maximize performance, only assign the Intrusion Prevention rules that are required by your policies and computers. You can use a recommendation scan to obtain a list of rules that are appropriate.
Although recommendation scans are performed for a specific computer, you can assign the recommendations to a policy that the computer uses.
For more information, see Manage and run recommendation scans.
- Open the properties for the computer to scan. Run the recommendation scan as described in Manually run a recommendation scan.You can configure Deep Security to Automatically implement recommendations scan results when it is appropriate to do so.
- Open the policy to which you want to assign the rules, and complete the rule assignments as described in Check scan results and manually assign rules.
To automatically and periodically fine tune your assigned Intrusion Prevention rules, you can schedule recommendation scans. See Schedule Deep Security to perform tasks.
Monitor your system
After you apply Intrusion Prevention rules, monitor system performance and Intrusion Prevention event logs.
Monitor system performance
Monitor CPU, RAM, and network usage to verify that system performance is still acceptable. If not, you can modify some settings and deployment aspects to improve performance (see Performance tips for intrusion prevention).
Check Intrusion Prevention events
Monitor Intrusion Prevention events to ensure that rules are not matching legitimate network traffic. If a rule is causing false positives you can unassign the rule. (See Assign and unassign rules.)
To see Intrusion Prevention events, click Events & Reports > Intrusion Prevention Events.
Enable 'fail open' for packet or system failures
The Intrusion Prevention module includes a network engine that might block packets before Intrusion Prevention rules can be applied. This might lead to downtime or performance issues with your services and applications. You can change this behavior so that packets are allowed through when system or internal packet failures occur. For details, see Enable 'fail open' behavior.
Switch to Prevent mode
When you are satisfied that Intrusion Prevention is not finding false positives, configure your policy to use Intrusion Prevention in Prevent mode so that rules are enforced and related events are logged, as follows:
- Go to Computer or Policy editor
 You can change these settings for a policy or for a specific computer.
To change the settings for a policy, go to the Polices page and double-click the policy that you want to edit (or select the policy and click Details).
To change the settings for a computer, go to the Computers page and double-click the computer that you want to edit (or select the computer and click Details). > Intrusion Prevention > General.
You can change these settings for a policy or for a specific computer.
To change the settings for a policy, go to the Polices page and double-click the policy that you want to edit (or select the policy and click Details).
To change the settings for a computer, go to the Computers page and double-click the computer that you want to edit (or select the computer and click Details). > Intrusion Prevention > General. - For Intrusion Prevention Behavior, select Prevent.
- Click Save.
Implement best practices for specific rules
HTTP Protocol Decoding rule
The HTTP Protocol Decoding rule is the most important rule in the Web Server Common application type. This rule decodes the HTTP traffic before the other rules inspect it. This rule also allows you to control various components of the decoding process.
This rule is required when you use any of the Web Application Common or Web Server Common rules that require it. Deep Security Manager automatically assigns this rule when it is required by other rules. As each web application is different, the policy that uses this rule should run in Detect mode for a period of time before switching to Prevent mode to determine if any configuration changes are required.
Changes to the list of illegal characters are often required.
For more information, see the following:
- HTTP protocol decoding in Deep Security
- Modifying the list of URI characters that Deep Security Agent considers illegal
- Illegal character in URI error appears in Deep Security
Cross-site scripting and generic SQL injection rules
Two of the most common application-layer attacks are SQL injection and cross-site scripting (XSS). Cross-site scripting and SQL injection rules intercept the majority of attacks by default, but you may need to adjust the drop score for specific resources if they cause false positives.
Both rules are smart filters that need custom configuration for web servers. If you have output from a Web Application Vulnerability Scanner, you should leverage that information when applying protection. For example, if the user name field on the login.asp page is vulnerable to SQL injection, ensure that the SQL injection rule is configured to monitor that parameter with a low threshold to drop on.
For more information, see Understanding the Generic SQL Injection Prevention rule.
Apply NSX security tags
Apply NSX security tags
Deep Security can apply NSX security tags to protected VMs when Intrusion Prevention rules are triggered. For details, see Configure Intrusion Prevention to apply NSX security tags.