Deep Security Manager 10 has reached end of support. Use the version selector (above) to see more recent versions of the Help Center.
Encrypt communication between the Deep Security Manager and the database
Communication between the Deep Security Manager and the database is not encrypted by default. This is for performance reasons and because the channel between the Manager and the database may already be secure (either they are running on the same computer or they are connected by crossover cable, a private network segment, or tunneling via IPSec).
However, if the communication channel between the Deep Security Manager and the database is not secure, you should encrypt the communications between them. Do this by editing the
dsm.properties
file located in
\Deep Security Manager\webclient\webapps\ROOT\WEB-INF\
Microsoft SQL Server (Linux)
To encrypt communication between the Deep Security Manager and a Microsoft SQL Server database:
- Stop the Deep Security Manager service:
# service dsm_s stop - Edit
/opt/dsm/webclient/webapps/ROOT/WEB-INF/dsm.propertiesto add the following line:database.SqlServer.ssl=require - Under
/opt/dsm, create a file nameddsm_s.vmoptionsthat contains the following line:-Djsse.enableCBCProtection=false - In the SQL Server Configuration Manager, enable "Force Encryption" in the protocol properties for the instance:
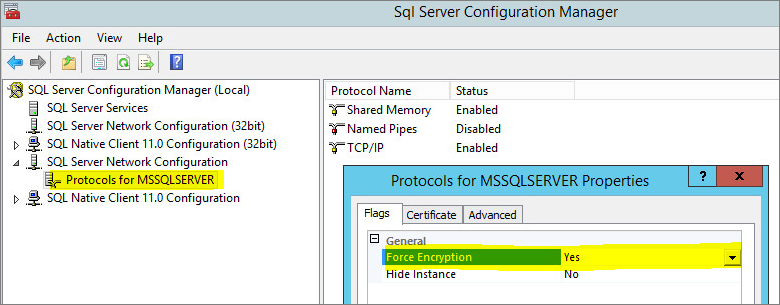
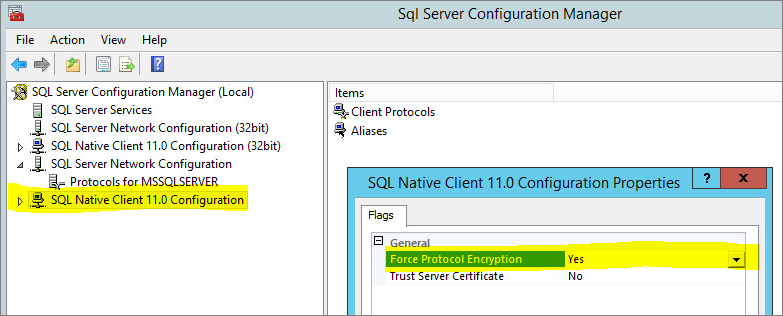
- Start the Deep Security Manager service:
# service dsm_s start
For additional information, see Enable Encrypted Connections to the Database Engine on the Microsoft MSDN site.
Microsoft SQL Server (Windows)
To encrypt communication between the Deep Security Manager and a Microsoft SQL Server database:
- Stop the Deep Security Manager service.
- Edit
\Program Files\Trend Micro\Deep Security Manager\webclient\webapps\ROOT\WEB-INF\dsm.propertiesto add the following line:database.SqlServer.ssl=require - Under
\Program Files\Trend Micro\Deep Security Manager, create a file namedDeep Security Manager.vmoptionsthat contains the following line:-Djsse.enableCBCProtection=false - In the SQL Server Configuration Manager, enable "Force Encryption" in the protocol properties for the instance:


- Start the Deep Security Manager service.
For additional information, see Enable Encrypted Connections to the Database Engine on the Microsoft MSDN site.
Oracle Database
To encrypt communication between the Deep Security Manager and an Oracle database:
- Add the following lines to
dsm.properties(example):
database.Oracle.oracle.net.encryption_types_client=(AES256)
database.Oracle.oracle.net.encryption_client=REQUIRED
database.Oracle.oracle.net.crypto_checksum_types_client=(SHA1)
database.Oracle.oracle.net.crypto_checksum_client=REQUIRED
- Save and close the file. Restart the Deep Security Manager service.
(All parameters prefixed with database.Oracle. will be passed to the Oracle driver.)
Possible values for the
encryption_types_client
are:
- AES256
- AES192
- AES128
- 3DES168
- 3DES112
- DES56C
- DES40C
- RC4_256
- RC4_128
- RC4_40
- RC4_56
Possible values for
crypto_checksum_types_client
are:
- MD5
- SHA1
For additional options consult: https://docs.oracle.com/cd/B28359_01/java.111/b31224/clntsec.htm
Running an Agent on the Database Server
Encryption should be enabled if you are using an Agent to protect the database. When you perform a Security Update, the Deep Security Manager stores new Intrusion Prevention Rules in the database. The rule names themselves will almost certainly generate false positives as they get parsed by the Agent if the data is not encrypted.