Deep Security Manager 10 has reached end of support. Use the version selector (above) to see more recent versions of the Help Center.
Identified files
This article covers how to access and work with identified files. For general best practices related to events, see Events in Deep Security.
To see the list of identified files, go to Events & Reports > Events > Anti-Malware Events > Identified Files.
An identified file is a file that has been found to be or to contain malware and has therefore been encrypted and moved to a special folder. ("Quarantine" is a scan action that you can specify when creating a Malware Scan Configuration.) Once the file has been identified or quarantined, you can choose to download it to your computer in an encrypted and compressed format. Whether or not an infected file is quarantined depends on the Anti-Malware Configuration that was in effect when the file was scanned.
After the identified file has been downloaded to your computer, the Identified File wizard will display a link to an Administration Utility which you can use to decrypt, examine, or restore the file.
A limited amount of disk space is set aside for storing identified files. The amount of space can be configured in Policy or Computer Editor > Anti-Malware > Advanced > Identified Files. Alerts are raised when there is not enough disk space to store an identified file.
If you are using a Deep Security Virtual Appliance to provide protection to virtual machines, all identified files from the Agentless VMs will be stored on the Virtual Appliance. As a result, you should increase the amount of disk space for identified files on the Virtual Appliance.
Identified files will be automatically deleted from a Virtual Appliance under the following circumstances:
- If a VM is moved to another ESXi host by vMotion, identified files associated with that VM will be deleted from the Virtual Appliance.
- If a VM is deactivated from the Deep Security Manager, identified files associated with that VM will be deleted from the Virtual Appliance.
- If a Virtual Appliance is deactivated from the Deep Security Manager, all the identified files stored on that Virtual Appliance will be deleted.
- If a Virtual Appliance is deleted from the vCenter, all the identified files stored on that Virtual Appliance will also be deleted.
The Identified Files page allows you to manage tasks related to identified files. Using the menu bar or the right-click context menu, you can:
-
 Restore only quarantined files back to their original location and condition.
Restore only quarantined files back to their original location and condition. -
 Download identified files from the computer
or Virtual Appliance to a location of your choice.
Download identified files from the computer
or Virtual Appliance to a location of your choice. -
 Analyze identified files from the computer
or Virtual Appliance to a location of your choice.
Analyze identified files from the computer
or Virtual Appliance to a location of your choice. -
 Delete one or more identified files from the computer
or Virtual Appliance.
Delete one or more identified files from the computer
or Virtual Appliance. -
 Export information about the identified file(s) (not the file itself) to a CSV file.
Export information about the identified file(s) (not the file itself) to a CSV file. -
 View the details of an identified file.
View the details of an identified file. -
 Computer Details displays the screen of the computer on which the malware was detected.
Computer Details displays the screen of the computer on which the malware was detected. -
 View Anti-Malware Event displays the anti-malware event associated with this identified file.
View Anti-Malware Event displays the anti-malware event associated with this identified file. -
 Add or Remove Columns by clicking Add/Remove.
Add or Remove Columns by clicking Add/Remove. -
 Search for a particular identified file.
Search for a particular identified file.
Details
The Identified File Details window displays more information about the file and lets you download the identified file to your computer or delete it where it is.
- Detection Time: The date and time on the infected computer that the infection was detected.
- Infected File(s): The name of the infected file.
- Malware: The name of the malware that was found.
- Scan Type: Indicates whether the malware was detected by a Real-time, Scheduled, or Manual scan.
- Action Taken: The result of the action taken by Deep Security when the malware was detected.
- Computer: The computer on which this file was found. (If the computer has been removed, this entry will read "Unknown Computer".)
Filter the list to search for an identified file
The Period tool bar allows you to filter the list to display only those files identified within a specific time frame.
The Computers tool bar allows you to organize the display of identified file entries by Computer Groups or Computer Policies.
Selecting "Open Advanced Search" from the "Search" menu toggles the display of the advanced search options:
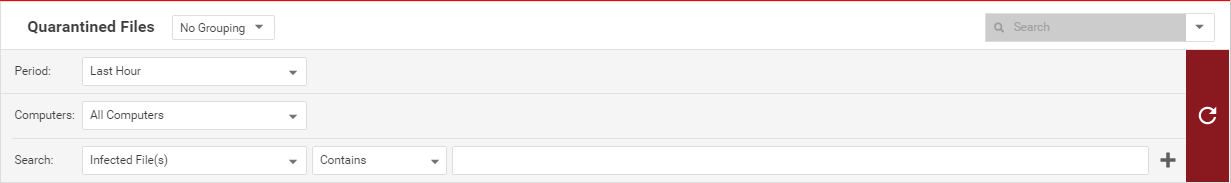
Advanced Search functions (searches are not case sensitive):
- Contains: The entry in the selected column contains the search string.
- Does Not Contain: The entry in the selected column does not contain the search string.
- Equals: The entry in the selected column exactly matches the search string.
- Does Not Equal: The entry in the selected column does not exactly match the search string.
- In: The entry in the selected column exactly matches one of the comma-separated search string entries.
- Not In: The entry in the selected column does not exactly match any of the comma-separated search string entries.
Pressing the "plus" button (+) to the right of the search bar will display an additional search bar so you can apply multiple parameters to your search. When you are ready, press the submit button (at the right of the tool bars with the right-arrow on it).
- Infected File: Shows the name of the infected file and the specific security risk.
- Malware: Names the malware infection.
- Computer: Indicates the name of the computer with the suspected infection.
Manually restore quarantined files
To manually restore a quarantined file, you must use the quarantined file decryption utility to decrypt the file and then move it back to its original location. The decryption utility is in a zip file, QFAdminUtil_win32.zip, located in the "util" folder under the Deep Security Manager root directory. The zipped file contains two utilities which perform the same function: QDecrypt.exe and QDecrypt.com. Running QDecrypt.exe invokes an open file dialog that lets you select the file for decryption. QDecrypt.com is a command-line utility with the following options:
- /h, --help: show this help message
- --verbose: generate verbose log messages
- /i, --in=<str>: quarantined file to be decrypted, where <str> is the name of the quarantined file
- /o, --out=<str>: decrypted file output, where <str> is the name given to the resulting decrypted file