Deep Security Manager 10 has reached end of support. Use the version selector (above) to see more recent versions of the Help Center.
Use a deployment script
Adding a computer to your list of protected resources in Deep Security and implementing protection is a multi-step process. Almost all of these steps can be performed from the command line on the computer and can therefore be scripted. The Deep Security Manager contains a deployment script writing assistant which can be accessed from Support menu.
- Go to Administration > System Settings > Agents.
- Select Allow Agent-Initiated Activation.
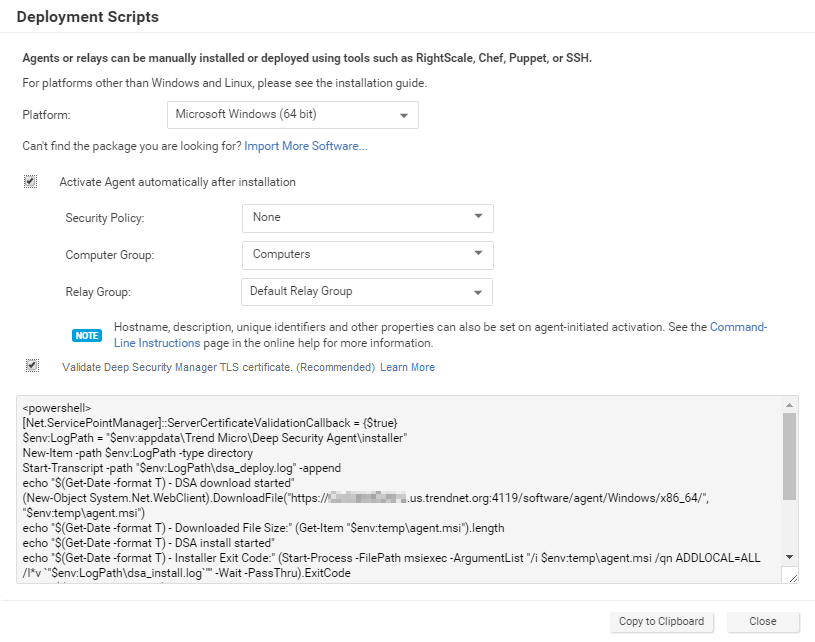
- In the top right corner, go to Support > Deployment Scripts.
-
Select the platform on which you are deploying the software.
Platforms in the menu correspond to software that you have imported into the Deep Security Manager from the Trend Micro Download Center. For information on importing Deep Security Software, see Update Deep Security software.
-
Select Activate agent automatically after installation.
To apply a policy, you must first activate the agent with its Deep Security Manager.
- Optionally, select the policy that you want to apply to the computer.
- Optionally, select the computer group that you want to assign to this computer.
- Optionally, select the relay group that you want the computer to use.
- Optionally (but highly recommended), select Validate Deep Security Manager TLS certificate.
When this option is selected, it checks that Deep Security Manager is using a valid TLS certificate from a trusted certificate authority (CA) when downloading the agent software, which can help prevent a “man in the middle” attack. You can check whether Deep Security Manager is using a valid CA certificate by looking at the browser bar in the Deep Security Manager console.
For Deep Security software installations only:By default, Deep Security Manager uses a self-signed certificate, which is not compatible with the Validate Deep Security Manager TLS certificate option. If your Deep Security Manager is not behind a load balancer, see Replace the Deep Security Manager TLS certificate for instructions on replacing the default self-signed certificate with a certificate from a trusted certificate authority. If the manager is behind a load balancer, you will need to replace the load balancer's certificates.
- The deployment script generator will display the script, which you can use in your preferred deployment tool.
If you are using Amazon Web Services and deploying new EC2 or VPC instances, copy the generated script and paste it into the User Data field. This will let you launch existing Amazon Machine Images (AMIs) and automatically install and activate the agent at startup. The new instances must be able to access the URLs specified in the generated deployment script. This means that your Deep Security Manager must be either Internet-facing, connected to AWS via VPN or Direct Link, or that your Deep Security Manager be deployed on Amazon Web Services too.
When copying the deployment script into the User Data field for a Linux deployment, copy the deployment script as-is into the "User Data" field and CloudInit will execute the script with sudo. (If there are failures, they will be noted in /var/log/cloud-init.log.)
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSCloudFormation/latest/UserGuide/deploying.applications.html
On Windows computers, the deployment script will use the same proxy settings as the local operating system. If the local operating system is configured to use a proxy and the Deep Security Manager is accessible only through a direct connection, the deployment script will fail.
Troubleshooting and tips
- For Deep Security software installations only: If you are attempting to run a deployment script and see exit code 2 "TLS certificate validation for the agent package download has failed. Please check that your Deep Security Manager TLS certificate is signed by a trusted root certificate authority. For more information, search for "deployment scripts" in the Deep Security Help Center.", the deployment script was created with the Validate Deep Security Manager TLS certificate checkbox selected. This error appears if Deep Security Manager is using a certificate that is not publicly trusted (such as the default self-signed certificate) for the connection between Deep Security Manager and its agents, or if there is a problem with a third-party certificate, such as a missing certificate in the trust chain between your certificate and the trusted CA. For information on certificates, see Replace the Deep Security Manager TLS certificate. As an alternative to replacing the trusted certificate, you can clear the Validate Deep Security Manager TLS certificate checkbox when generating a deployment script. Note that this is not recommended for security reasons.