Deep Security 11.1 has reached end of support. Use the version selector (above) to see more recent versions of the Help Center.
Firewall settings with Oracle RAC
Deep Security supports:
- SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 11 SP3 with Oracle RAC 12c Release 1 (v12.1.0.2.0)
- Red Hat Linux Enterprise Server 6.6 with Oracle RAC 12c Release 1 (v12.1.0.2.0)
- Red Hat Linux Enterprise Server 7.0 with Oracle RAC 12c Release 1 (v12.1.0.2)
The default Linux Server Deep Security policy is compatible with the Oracle RAC environment, with the exception of firewall settings. Because there are complex communication channels between RAC nodes, the RAC nodes will fail to create a virtual NIC and scan the NIC, due to firewall interference. As a result, Oracle Clusterware would fail to start on some nodes. You can disable the firewall or customize the firewall settings.
Add a rule to allow communication between nodes
- In the Deep Security Manager, go to the Policies tab.
- Right-click the Linux Server policy and click Duplicate.
- Click the new Linux Server_2 policy and click Details.
- Give the policy a new name, for example, "Oracle RAC" and click Save.
- Click Firewall.
- Click Assign/Unassign.
- Click New > New Firewall Rule.
- Under General Information, set the Name to something descriptive, like "Allow communication with Oracle nodes". Set Action to "Force Allow" and set Protocol to "Any".
- Under Packet Source, set MAC to "MAC List". In the Select MAC List that appears, select "New". A "New MAC List Properties" dialog box appears.
- Give the MAC list a name, like "Oracle RAC MAC list". Under MAC(s): (One MAC per line), add all of the MAC addresses used by all Oracle nodes (including MACs from both private and public NICs). Click OK when finished.
- Under Packet Destination, set MAC to "MAC List". In the Select MAC List that appears, select the MAC list you created in step 10 and then click OK.
- In the Firewall Rules list for the policy, ensure that this new rule is selected and click OK and then click Save.
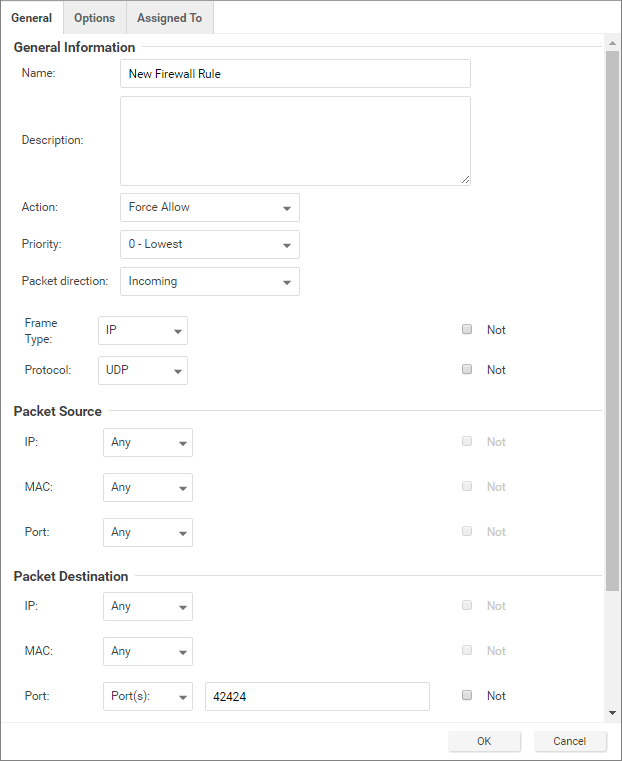
Add a rule to allow UDP port 42424
Follow the steps described in the procedure above to add a new rule that allows UDP port 42424. This port number is used by the Cluster Synchronization Service daemon (CSSD), Oracle Grid Interprocess Communication (GIPCD) and Oracle HA Services daemon (OHASD).
Please note that the MAC list that you created above may not be able to cover this rule. This rule is essential for Oracle RAC.
Allow other RAC-related packets
Oracle RAC will send a very large number of packets with Frame Type C08A and 0ACB. Blocking them may cause some unpredictable behavior.
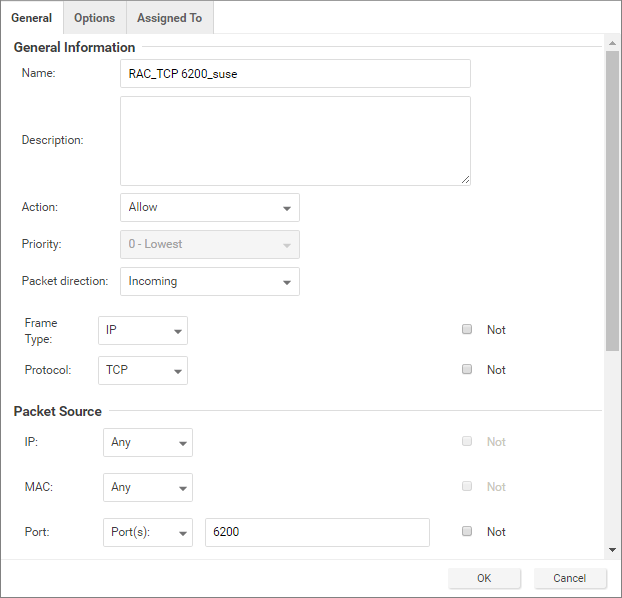
- Allow TCP post 6200: Add the public IP addresses of the RAC nodes in the IP fields under Packet Source and Packet Destination and set destination port to 6200. This port number is used by Oracle Notification Services (ONS). This port is configurable, so check the value on your system set the correct port number if it is something other than 6200.
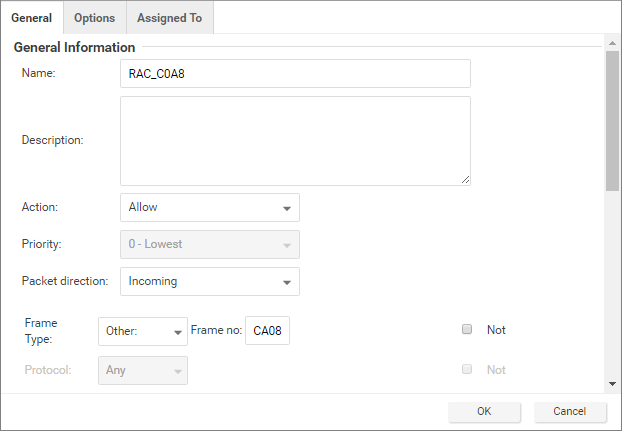
- Allow Frame Type C0A8: Add a rule with the Frame Type set to "Other" and the Frame no set to "C0A8".
- Allow Frame Type 0ACB: Add a rule with the Frame Type set to "Other" and the Frame no set to "0ACB".
- Allow Frame Type 0AC9: Add a rule with the Frame Type set to "Other" and the Frame no set to "0AC9".
- Allow IGMP protocol: Add a rule with the Protocol set to "IGMP".

Please refer to the following link to check whether there are additional RAC-related components in your system that need extra firewall rules to allow certain ports:
https://docs.oracle.com/database/121/RILIN/ports.htm#RILIN1178
Ensure that the Oracle SQL Server rule is assigned
Check that the "Oracle SQL Server" Firewall rule is assigned to the Linux Server policy. This is a pre-defined Deep Security Firewall rule that allows port 1521.
Ensure that anti-evasion settings are set to "Normal"
In the properties for the Linux Server policy, Settings > Network Engine > Anti-Evasion Settings are set to "Normal" by default. If this setting is set to "Strict", the RAC database response will be extremely slow.
