Deep Security 10.3 has reached end of support. Use the version selector (above) to see more recent versions of the Help Center.
Use deployment scripts to add and protect computers
Adding a computer to your list of protected resources in Deep Security and implementing protection is a multi-step process. Almost all of these steps can be performed from the command line on the computer and can therefore be scripted. The Deep Security Manager contains a deployment script writing assistant which can be accessed from the Support menu.
- Go to Administration > System Settings > Agents.
- Select Allow Agent-Initiated Activation.
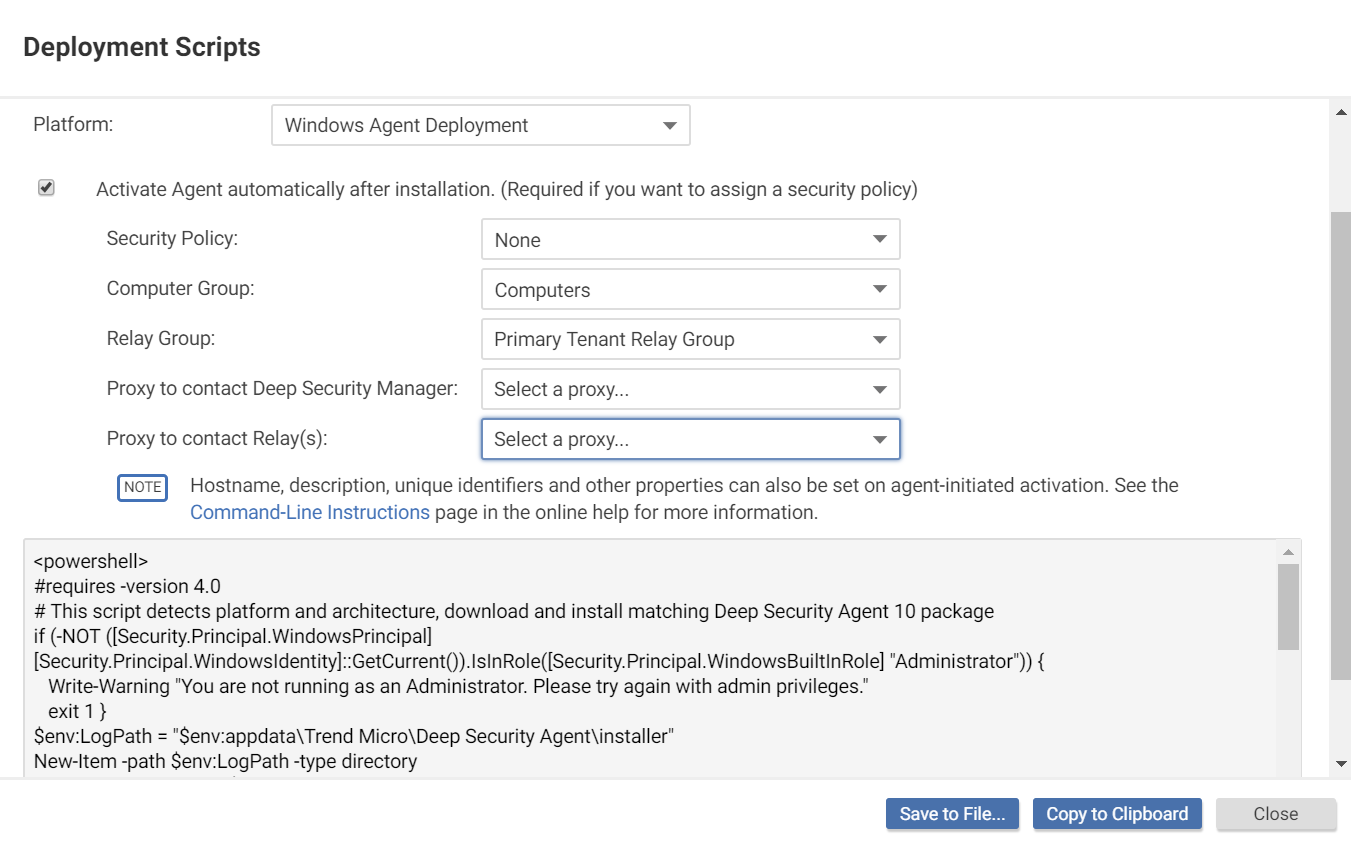
- In the top right corner, go to Support > Deployment Scripts.
-
Select the platform on which you are deploying the software.
Platforms in the menu correspond to software that you have imported into the Deep Security Manager from the Trend Micro Download Center. For information on importing Deep Security Software, see Update Deep Security software.
-
Select Activate agent automatically after installation.
To apply a policy, you must first activate the agent with its Deep Security Manager.
- Optionally, select the Security Policy, Computer Group, Relay Group, Proxy to contact Deep Security Manager, and Proxy to contact Relay(s).
- The deployment script generator will display the script. Click Copy to Clipboard and paste the deployment script in your preferred deployment tool, or click Save to File.
If you are using Amazon Web Services and deploying new Amazon EC2, Amazon WorkSpace, or VPC instances, copy the generated script and paste it into the User Data field. This will let you launch existing Amazon Machine Images (AMIs) and automatically install and activate the agent at startup. The new instances must be able to access the URLs specified in the generated deployment script. This means that your Deep Security Manager must be either Internet-facing, connected to AWS via VPN or Direct Link, or that your Deep Security Manager be deployed on Amazon Web Services too.
When copying the deployment script into the User Data field for a Linux deployment, copy the deployment script as-is into the "User Data" field and CloudInit will execute the script with sudo. (If there are failures, they will be noted in /var/log/cloud-init.log.)
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSCloudFormation/latest/UserGuide/aws-properties-waitcondition.html
Troubleshooting and tips
- If you are attempting to deploy the agent from PowerShell (x86), you will receive the following error : C:\Program Files (x86)\Trend Micro\Deep Security Agent\dsa_control' is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet, function, script file, or operable program. Check the spelling of the name, or if a path was included, verify that the path is correct and try again.
The PowerShell script expects the environment variable for ProgramFiles to be set to "Program Files", not "Program Files (x86)". To resolve the issue, close PowerShell (x86) and run the script in PowerShell as an administrator.
- If you do not intend to enable anti-malware protection on your computers, you may want to prevent the installation of the anti-malware engine entirely. To do so, delete the string "ADDLOCAL=ALL" from the deployment script.
- On Windows computers, the deployment script will use the same proxy settings as the local operating system. If the local operating system is configured to use a proxy and the Deep Security Manager is accessible only through a direct connection, the deployment script will fail.