Deep Security 10.1 has reached end of support. Use the version selector (above) to see more recent versions of the Help Center.
Protect servers from malware in four steps
To use anti-malware, the basic steps are:
- Turn on the anti-malware module.
- Select the types of scans you want.
- Configure scan settings and options.
- Ensure that Deep Security can keep up to date on the latest threats.
Turn on the anti-malware module
- Go to Policies.
- Double-click the policy you want to enable anti-malware.
- Go to Anti-Malware > General.
- From Anti-Malware State, select On.
Select the types of scans you want
When anti-malware has been turned on, Deep Security needs to know what type of scans it should perform. You can configure this on Anti-Malware > General in the Computer editor![]() To open the Computer editor, go to the Computers page and double-click the computer that you want to edit (or select the computer and click Details)..
To open the Computer editor, go to the Computers page and double-click the computer that you want to edit (or select the computer and click Details)..
| Type | Description | Scan Settings | When Run |
|---|---|---|---|
| Real-Time Scan | A persistent and ongoing scan. Each time a file is received, opened, downloaded, copied, or modified, Deep Security scans the file for security risks. If Deep Security detects no security risk, the file remains in its location and users can proceed to access the file. If Deep Security detects a security risk, it displays a notification message that shows the name of the infected file and the specific security risk. This scan can be run on all platforms supported by the anti-malware module. |
Uses the selected malware scan configuration Click Edit to modify the settings or go to policies > common objects > Other > Malware Scan Configurations to create a new scan configuration. |
Every Day All Day unless another time period is configured using the Schedule option Tip: You can configure real-time scanning to run when it will not have a large impact on performance; for example, when a file server is scheduled to back up files. |
| Manual Scan | Runs a full system scan on all processes and files on a computer. The time it takes to complete depends on the number of files to scan and the computer's hardware resources. Takes longer to complete than a Quick Scan. This scan can be run on all platforms supported by the anti-malware module. |
Uses the selected malware scan configuration Click Edit to modify the settings or go to Policies > Common Objects > Other > Malware Scan Configurations to create a new scan configuration. |
When Full Scan for Malware is clicked |
| Scheduled Scan | Runs automatically on the appointed date and time. Use scheduled scan to automate routine scans and improve scan management efficiency. This scan can be run on all platforms supported by the anti-malware module. |
Uses the selected malware scan configuration Click Edit to modify the settings or go to Policies > Common Objects > Other > Malware Scan Configurations to create a new scan configuration. |
According to the date and time you specify when you create a Scan computers for Malware task using scheduled tasks (Administration > Scheduled Tasks) |
| Quick Scan | Only scans a computer's critical system areas for currently active threats. A Quick Scan will look for currently active malware but it will not perform deep file scans to look for dormant or stored infected files. It is significantly faster than a Full Scan on larger drives. This scan can only be run on Windows servers. |
Not configurable | When Quick Scan for Malware is clicked |
Scan objects and sequence
The following table lists the objects scanned during each type of scan and the sequence in which they are scanned.
| Targets | Full Scan (Manual or Scheduled) | Quick Scan |
|---|---|---|
| Drivers | 1 | 1 |
| Trojan | 2 | 2 |
| Process Image | 3 | 3 |
| Memory | 4 | 4 |
| Boot Sector | 5 | - |
| Files | 6 | 5 |
| Spyware | 7 | 6 |
Configure scan settings and options
The following section provides recommendations and information about some of the key settings and options for running anti-malware scans. For detailed information about all available settings, see Anti-malware settings and Malware Scan Configurations.
Anti-malware configuration settings to maximize performance
The following actions are recommended to maximize the performance of the Deep Security anti-malware module:
- Ensure that the real-time scan is enabled (see Select the types of scans you want).
- Set up the proper exclusion list to exclude the folder, file, or extensions and add the UNC path into the exclusion list (see Scan exclusions).
- Set the Scan Limitation to prevent scanning a file larger than the specified size (anti-malware > Advanced in the Computer editor
 To open the Computer editor, go to the Computers page and double-click the computer that you want to edit (or select the computer and click Details).).
To open the Computer editor, go to the Computers page and double-click the computer that you want to edit (or select the computer and click Details).). - Enable the scan cache and change the cache time based on your real situation (see Virtual Appliance Scan Caching).
Scan Configuration Settings
The tables below show the recommended settings for each scan configuration. Information on recommendations for scan exclusions is provided in Scan exclusions.
You can specify which files and directories are included or excluded during a scan and which actions are taken if malware is detected on a computer (for example, clean, quarantine, or delete) by editing the malware scan configuration associated with the scan type. Deep Security comes with default malware scan configurations for each type of scan, which are used in Deep Security's default security policies.
- Go to Policies > Common Objects > Other > Malware Scan Configuration.
- Double-click the scan configuration you want to edit, or click New to create a new one.
From this page, you can modify an existing scan configuration or create a new one. For more information, see Malware Scan Configurations.
Recommended real-time scan configuration
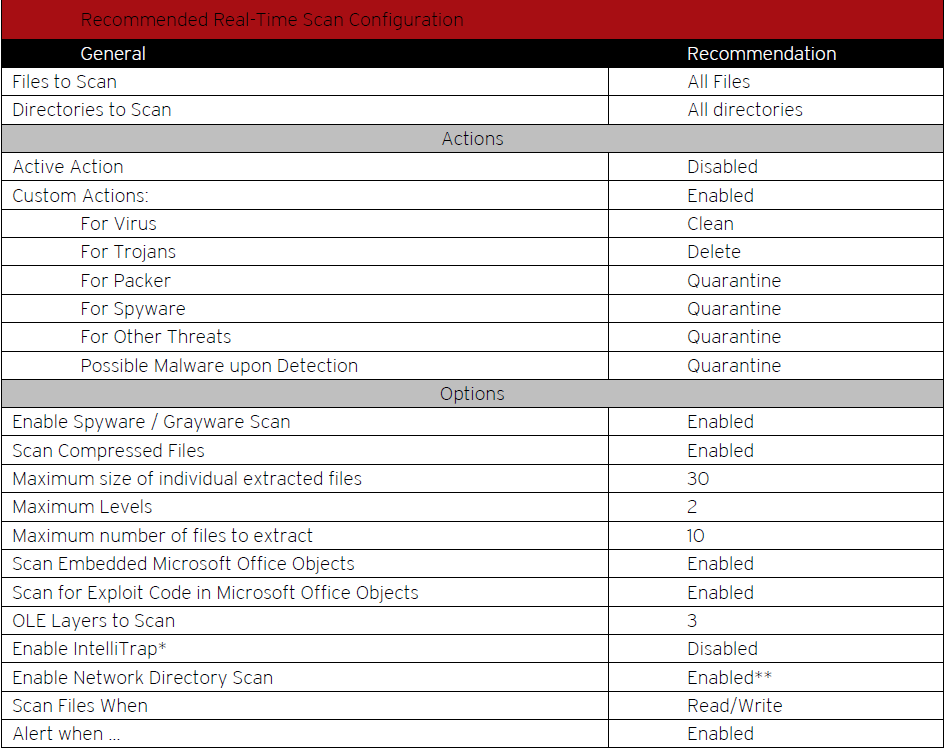
* Virus writers often attempt to circumvent virus filtering by using real-time compression algorithms. IntelliTrap helps reduce the risk of such viruses entering your network by blocking real-time compressed executable files and pairing them with other malware characteristics. Since IntelliTrap identifies such files as security risks and might incorrectly block safe files, you can disable IntelliTrap if users regularly exchange real-time compressed executable files. (IntelliTrap only works in Real-Time mode.)
** Network directory scanning should be disabled to maintain maximum performance during a Real-Time Scan. However, these network resources must be protected by a local anti-virus scanner. Leave this enabled if there is no other file scanner for network shares.
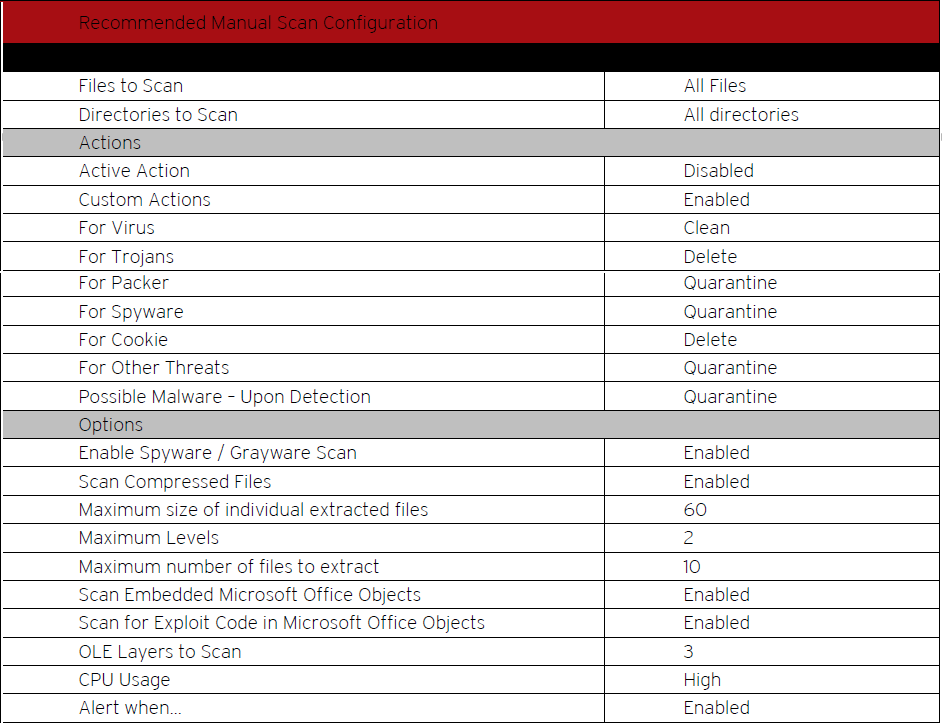
Recommended Manual Scan Configuration
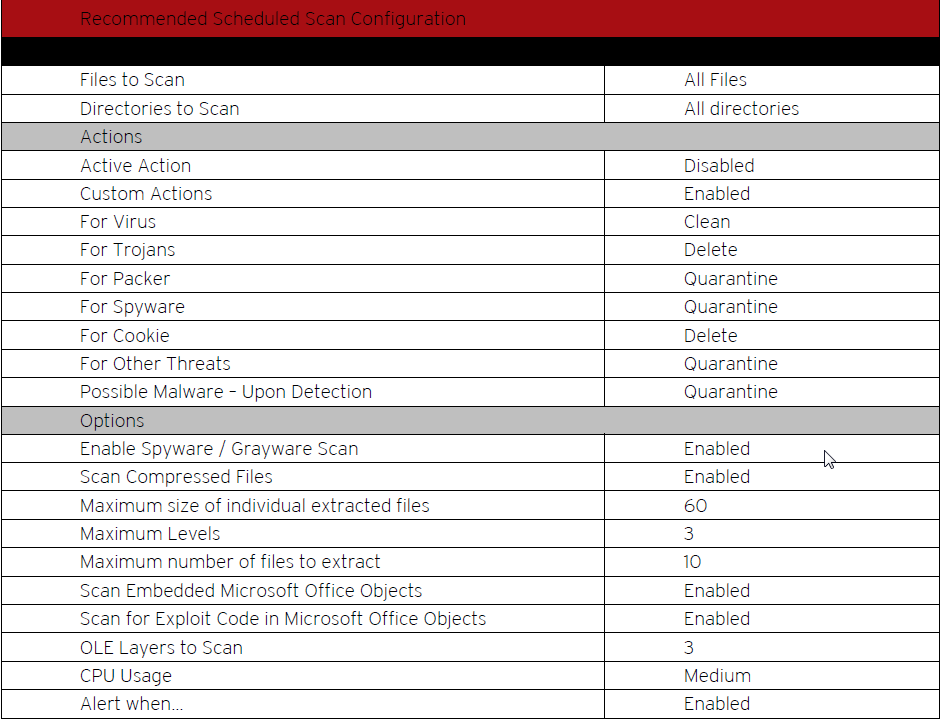
Recommended scheduled scan configuration
Scan exclusions
To reduce scanning time and minimize the use of computing resources, you can configure Deep Security malware scans to exclude specific folders, files, and file types from all types of scans. You can also exclude process image files from real-time malware scans that are run on Windows servers.
All of these exclusions are specified by selecting exclusion lists on the Exclusions tab of the Malware Scan Configuration editor. You can create and modify these lists by going to Policies > Common Objects > Lists.
If any performance-related issues are experienced when Deep Security anti-malware protection is enabled, you can use exclusions to help troubleshoot these issues by excluding specific folders or files from scanning.
Scan exclusion recommendations
The best and most comprehensive source for scan exclusions is from the software vendor. The following are some high-level scan exclusion recommendations:
- Quarantine folders (such as SMEX on Microsoft Windows Exchange Server) should be excluded to avoid rescanning files that have already been confirmed to be malware.
- Large databases and database files (for example, dsm.mdf and dsm.ldf) should be excluded because scanning could impact database performance. If it is necessary to scan database files, you can create a scheduled task to scan the database during off-peak hours. Since Microsoft SQL Server databases are dynamic, exclude the directory and backup folders from the scan list:
${ProgramFiles}\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL\Data\
${Windir}\WINNT\Cluster\ # if using SQL Clustering
Q:\ # if using SQL Clustering
For a list of recommended scan exclusions, see the Trend Micro recommended scan exclusion list. Microsoft also maintains an Anti-Virus Exclusion List that you can use as a reference for excluding files from scanning on Windows servers.
Smart Scan
Enabling Smart Scan provides several benefits:
- Provides fast, cloud-based, real-time security status lookups
- Reduces the time required to deliver protection against emerging threats
- Reduces network bandwidth consumed during pattern updates (bulk of pattern definition updates only need to be delivered to the cloud, not to many computers)
- Reduces cost and overhead of corporate-wide pattern deployments
- Lowers kernel memory consumption on computers (consumption increases minimally over time)
Smart Scan uses threat signatures that are stored on Trend Micro servers. When Smart Scan is enabled, Deep Security first scans locally for security risks. If Deep Security cannot assess the risk of the file during the scan, it will try to connect to a local Smart Scan server. If no local Smart Scan Server is detected, Deep Security will attempt to connect to the Trend Micro Global Smart Scan server. For more information on this feature, see Smart Protection in Deep Security.
- ds100-en.url.trendmicro.com
- https://ds10.icrc.trendmicro.com/tmcss/?
- Go to Policies.
- Double-click a policy.
- Go to Anti-Malware > Smart Protection.
-
In the Smart Scan section, either:
- select Inherited (if the parent policy has Smart Scan enabled)
- deselect Inherited, and then select either On or On for Deep Security Agent, Off for Virtual Appliance.
- Click Save.
Quarantine settings
The default quarantine file settings are the recommended settings. To view them, in the Computer editor![]() To open the Computer editor, go to the Computers page and double-click the computer that you want to edit (or select the computer and click Details)., go to Anti-Malware > Advanced.
To open the Computer editor, go to the Computers page and double-click the computer that you want to edit (or select the computer and click Details)., go to Anti-Malware > Advanced.
Maximum disk space used to store quarantined files determines how much disk space can be used to store quarantined files. You can change this setting in the policy, or override it for individual computers.
Resource allocation for malware scans
Real-time scans use multi-threaded processing for scans by default. But you can also configure manual and scheduled scans to use multi-threaded processing to improve the performance of physical computers.
Do not enable multi-threaded processing if:
- resources are limited (for example, CPU-bound tasks)
- resources should be held by only one operator at a time (for example, IO-bound tasks)
- Go to Policies.
- Double-click to open the policy where you want to enable multi-threaded processing.
- Go to Anti-Malware > Advanced.
- In the Resource Allocation for Malware Scans section, select Yes.
- Restart the computers on which you enabled multi-threaded processing for the setting to take effect.
Ensure that Deep Security can keep up to date on the latest threats
To remain effective against new viruses and exploits, Deep Security agents need to be able to download the latest software and security update packages from Trend Micro or indirectly, from your own Relay. These packages contain threat definitions and patterns. Relay-enabled agents, organized into relay groups (also managed and configured by the Deep Security Manager) retrieve security updates from Trend Micro, and then distribute them to other agents and appliances.
- Go to Administration > System Settings > Updates.
- Configure Deep Security's ability to retrieve security updates from Trend Micro. Make sure you have at least one relay-enabled agent, and it is assigned to the appropriate agents and appliances.
To determine if a Deep Security Agent is a relay, next to a computer, click Preview.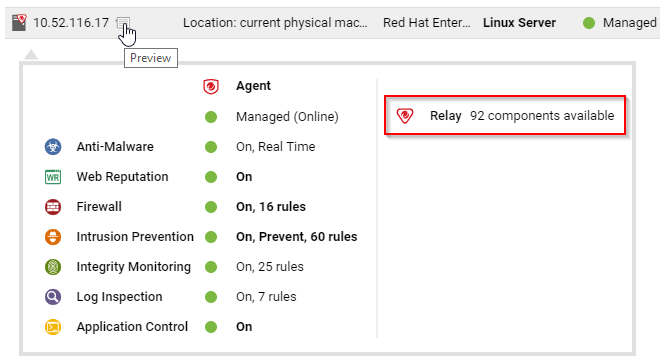
- Go to Administration > Scheduled Tasks.
- Verify that there is a scheduled task to regularly download available updates for both security and software updates.