Deep Security 10.1 has reached end of support. Use the version selector (above) to see more recent versions of the Help Center.
Firewall events
This article covers how to access and work with firewall events. For general best practices related to events, see Events in Deep Security.
To see the firewall events captured by Deep Security, go to Events & Reports > Events > Firewall Events.
Firewall event icons:
-
 Single event
Single event -
 Single event with data
Single event with data -
 Folded event
Folded event -
 Folded event with data
Folded event with data
What information is displayed for firewall events?
These columns can be displayed on the firewall events page. You can click Columns to select which columns are displayed in the table.
- Time: Time the event took place on the computer.
- Computer: The computer on which this event was logged. (If the computer has been removed, this entry will read "Unknown Computer".)
- Reason: Log entries on this page are generated either by firewall rules or by firewall stateful configuration settings. If an entry is generated by a firewall rule, the column entry will be prefaced by "Firewall Rule:" followed by the name of the firewall rule. Otherwise the column entry will display the firewall stateful configuration setting that generated the log entry.
- Tag(s): Event tags that are applied to this event.
- Action: The action taken by the firewall rule or firewall stateful configuration. Possible actions are: Allow, Deny, Force Allow, and Log Only.
- Rank: The ranking system provides a way to quantify the importance of intrusion prevention and firewall events. By assigning "asset values" to computers, and assigning "severity values" to intrusion prevention rules and firewall rules, the importance ("rank") of an event is calculated by multiplying the two values together. This allows you to sort events by rank when viewing intrusion prevention or firewall events.
- Direction: The direction of the affected packet (incoming or outgoing).
- Interface: The MAC address of the interface through which the packet was traveling.
- Frame Type: The frame type of the packet in question. Possible values are "IPV4", "IPV6", "ARP", "REVARP", and "Other: XXXX" where XXXX represents the four digit hex code of the frame type.
- Protocol: Possible values are "ICMP", "ICMPV6", "IGMP", "GGP", "TCP", "PUP", "UDP", "IDP", "ND", "RAW", "TCP+UDP", AND "Other: nnn" where nnn represents a three digit decimal value.
- Flags: Flags set in the packet.
- Source IP: The packet's source IP.
- Source MAC: The packet's source MAC address.
- Source Port: The packet's source port.
- Destination IP: The packet's destination IP address.
- Destination MAC: The packet's destination MAC address.
- Destination Port: The packet's destination port.
- Packet Size: The size of the packet in bytes.
- Repeat Count: The number of times the event was sequentially repeated.
- Time (microseconds): Microsecond resolution for the time the event took place on the computer.
- Event Origin: The Deep Security component from which the event originated.
See details about an event
Double-clicking an event (or right-clicking an event and clicking View) displays a window that contains additional information about the event. The Tags tab displays tags that have been attached to this event. For more information on event tagging, see Apply tags to identify and group events.
You can also right-click an event and select Computer Details to open the Computer editor for the computer that generated the event.
Find a particular event
You can use the lists at the top of each events page to filter and group the events. Select the values that you want to filter for and then click the large search button on the right side to apply the filter. You can also use the search bar in the upper-right corner to search for a specific event.
To perform an advanced search, click the arrow in the Search bar and select Open Advanced Search.
The Period setting lets you filter the list to display only those events that occurred within a specific time-frame.
The Computers setting lets you organize the display of event log entries by computer, computer groups or policies.
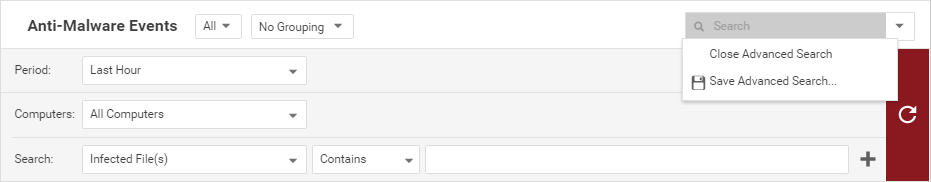
Advanced Search functions (searches are not case sensitive):
- Contains: The entry in the selected column contains the search string
- Does Not Contain: The entry in the selected column does not contain the search string
- Equals: The entry in the selected column exactly matches the search string
- Does Not Equal: The entry in the selected column does not exactly match the search string
- In: The entry in the selected column exactly matches one of the comma-separated search string entries
- Not In: The entry in the selected column does not exactly match any of the comma-separated search string entries
Pressing the "plus" button (+) to the right of the search bar will display an additional search bar so you can apply multiple parameters to your search. When your search parameters are ready, click the large blue arrow on the right side.
Export a list of events
Clicking Export exports all or selected events to a CSV file.
Tag events
Clicking Auto-Tagging displays a list of existing auto-tagging rules that have been applied to the events. You can also right-click an event to manually add or remove tags. (See Apply tags to identify and group events.)