Deep Security 10.1 has reached end of support. Use the version selector (above) to see more recent versions of the Help Center.
Anti-malware events
This article covers how to access and work with anti-malware events. For general best practices related to events, see Events in Deep Security.
To see the anti-malware events captured by Deep Security, go to Events & Reports > Events > Anti-Malware Events.
What information is displayed for anti-malware events?
These columns can be displayed on the Anti-Malware Events page. You can click Columns to select which columns are displayed in the table.
- Time: Time the event took place on the computer.
- Computer: The computer on which this event was logged. (If the computer has been removed, this entry will read "Unknown Computer".)
- Infected File(s): The location and name of the infected file.
- Tag(s): Event tags associated with this event.
- Malware: The name of the malware that was found.
- Action Taken: Displays the results of the actions specified in the malware scan configuration associated with the event.
- Cleaned:Deep Security successfully terminated processes or deleted registries, files, cookies, or shortcuts, depending on the type of malware.
- Clean Failed: Malware could not be cleaned for a variety of possible reasons.
- Deleted: An infected file was deleted.
- Delete Failed: An infected file could not be deleted for a variety of possible reasons. For example, the file may be locked by another application, is on a CD, or is in use. If possible, Deep Security will delete the infected file once it is released.
- Quarantined: An infected file was moved to the identified files folder.
- Quarantine Failed: An infected file could not be quarantined for a variety of possible reasons. For example, the file may be locked by another application, is on a CD, or is in use. If possible, Deep Security will quarantine the infected file once it is released. It is also possible that the "Maximum disk space used to store identified files" (specified on the Policy/Computer Editor > Anti-Malware > Advanced tab) has been exceeded.
- Access Denied: Deep Security has prevented the infected file from being accessed without removing the file from the system.
- Passed: Deep Security did not take any action but logged the detection of the malware.
- Scan Type: The type of scan that found the malware (Real-Time, Scheduled, or Manual).
- Event Origin: Indicates from which part of the Deep Security system the event originated.
- Reason: The malware scan configuration that was in effect when the malware was detected.
- Major Virus Type: The type of malware detected. Possible values are: Joke, Trojan, Virus, Test, Spyware, Packer, Generic, or Other. For information on these types of malware, see the anti-malware event details or see What types of malware does Deep Security protect against?
- Target(s): The file, process, or registry key (if any) that the malware was trying to affect. If the malware was trying to affect more than one, this field will contain the value "Multiple."
- Target Type: The type of system resource that this malware was trying to affect, such as the file system, a process, or Windows registry.
- Container ID: ID of the Docker container where the malware was found.
- Container Image Name: Image name of the Docker container where the malware was found.
- Container Name: Name of the Docker container where the malware was found.
- File MD5: The MD5 hash of the file.
See details about an event
Double-clicking an event (or right-clicking an event and clicking View) displays a window that contains additional information about the event. The Tags tab displays tags that have been attached to this event. For more information on event tagging, see Apply tags to identify and group events.
You can also right-click an event and select Computer Details to open the Computer editor for the computer that generated the event.
If the action associated with the event was quarantined, you can right-click the event and select Identified File Details to see details about the file associated with this event.
Find a particular event
You can use the lists at the top of each events page to filter and group the events. Select the values that you want to filter for and then click the large search button on the right side to apply the filter. You can also use the search bar in the upper-right corner to search for a specific event.
To perform an advanced search, click the arrow in the Search bar and select Open Advanced Search.
The Period setting lets you filter the list to display only those events that occurred within a specific time-frame.
The Computers setting lets you organize the display of event log entries by computer, computer groups or policies.
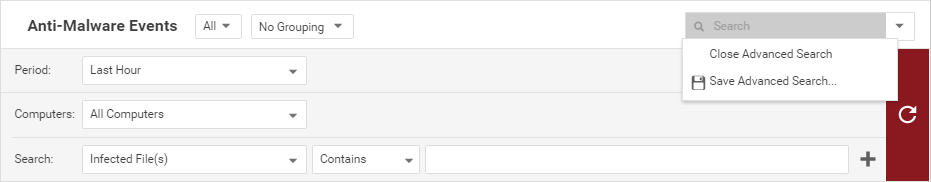
Advanced Search functions (searches are not case sensitive):
- Contains: The entry in the selected column contains the search string
- Does Not Contain: The entry in the selected column does not contain the search string
- Equals: The entry in the selected column exactly matches the search string
- Does Not Equal: The entry in the selected column does not exactly match the search string
- In: The entry in the selected column exactly matches one of the comma-separated search string entries
- Not In: The entry in the selected column does not exactly match any of the comma-separated search string entries
Pressing the "plus" button (+) to the right of the search bar will display an additional search bar so you can apply multiple parameters to your search. When your search parameters are ready, click the large blue arrow on the right side.
Export a list of events
Clicking Export exports all or selected events to a CSV file.
Tag events
Clicking Auto-Tagging displays a list of existing auto-tagging rules that have been applied to the events. You can also right-click an event to manually add or remove tags. (See Apply tags to identify and group events.)